Healthcare Interoperability Solutions: Addressing Challenges for Seamless Integration
May 13, 2024
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, the requirement for efficient data exchange and collaboration among diverse platforms and providers becomes increasingly crucial. However, with progress, challenges are bound to happen and one of them is improving interoperability. To overcome such challenges, it is important to understand healthcare interoperability solutions to ensure that patient data flows seamlessly and securely across various healthcare systems.
Did you know, according to ONC, almost 48% of hospitals suffer from one-sided data exchange as they share the data with other providers and never receive the same?
Similarly, there are various health interoperability challenges which we will discuss further with suitable solutions.
Key Healthcare Interoperability Challenges and Solutions
Interoperability encounters various challenges which need to be addressed to ensure a smooth and efficient healthcare ecosystem.
Let’s explore some of these challenges with viable solutions given for each:
Challenge 1: Technical Issues
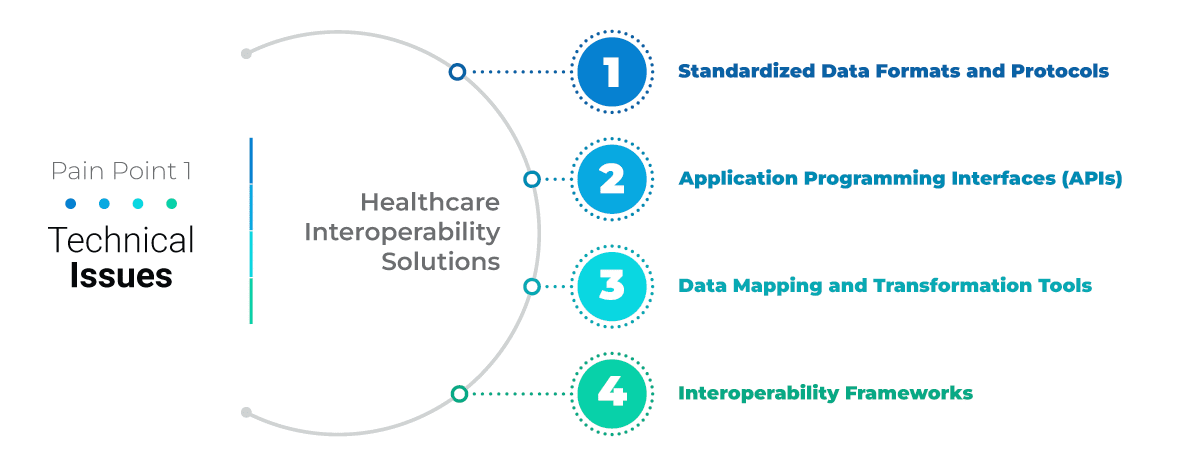
The healthcare industry is heavily dependent on the variety of software systems and devices which manage patient records, diagnostic tools, treatment plans, and administrative tasks. The varying standards, protocols, and data formats of these technologies pose a challenge to achieve a seamless data exchange. For instance, Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), laboratory information systems, and billing systems; all use different formats and communication protocols.
Healthcare Interoperability Solutions
Standardized Data Formats and Protocols: Standardized data formats such as Health Level Seven (HL7) and Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) can facilitate interoperability. These standards define how healthcare information should be structured, exchanged, and managed across systems to ensure that data is consistent and compatible.
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs): APIs enable seamless communication and data sharing between different healthcare systems. APIs act as intermediaries that allow applications to interact with each other and provide a standardized way for systems to exchange data irrespective of their technologies.
Data Mapping and Transformation Tools: Data mapping and transformation tools can convert data from one format to another. These tools can translate data elements, terminology, and coding schemes which enables interoperability between systems with different data structures.
Interoperability Frameworks: Interoperability frameworks define common rules, guidelines, and best practices for data exchange. Frameworks such as Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise (IHE) promote interoperability by addressing technical, semantic, and organizational aspects of data sharing.
Challenge 2: Isolated EHR Systems

Fragmented Patient Data: Isolated EHR systems result in fragmented patient data which makes it difficult for healthcare providers to access medical histories, treatment plans, and diagnostic information.
Inefficient Care Delivery: Without seamless data exchange between systems, healthcare teams face challenges in coordinating care, sharing critical information, and making informed clinical decisions. It leads to inefficiencies in care delivery and patient outcomes.
Limited Interoperability: Isolated EHR systems often lack interoperability standards, protocols, and integration capabilities which hinders the seamless flow of patient data across different healthcare settings and platforms.
Healthcare Interoperability Solutions
Interoperable EHR Systems: Migrating to interoperable EHR systems supports standardized data formats, protocols, and APIs for uninterrupted data exchange. Interoperable systems enable healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient records, collaborate with multidisciplinary teams, and deliver coordinated care across the continuum.
Health Information Exchange (HIE) Networks: HIE networks facilitate secure data sharing and interoperability among healthcare organizations. HIE networks allow real-time access to patient data, reduce duplication of tests and procedures, and improve care coordination and transitions.
Data Integration Platforms: Data integration platforms can centralize and standardize patient data from various sources, such as EHR systems, laboratory systems, imaging systems, and wearable devices. These platforms enable data aggregation, normalization, and analytics, and support clinical decision-making and population health management.
Collaborative Partnerships: Collaborating with EHR vendors, healthcare IT companies, and industry stakeholders can develop healthcare interoperability solutions, standards, and best practices. Interoperability initiatives, such as the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standard can promote data exchange, interoperability, and innovation in healthcare technology.
Challenge 3: Privacy Concerns
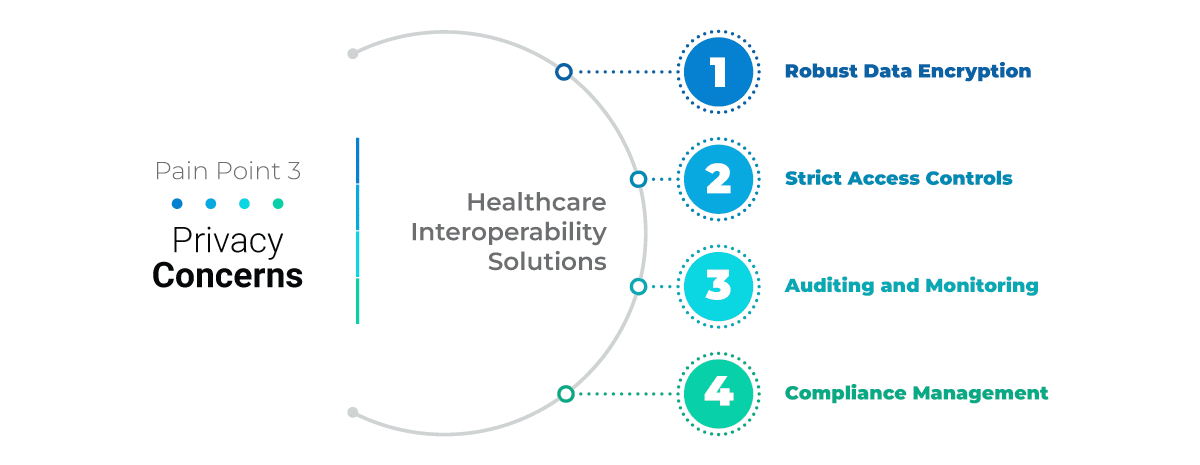
Data Breaches and Cybersecurity Threats: The healthcare sector is a prime target for cyberattacks due to the valuable patient information stored in electronic health records (EHRs) and other healthcare systems. Data breaches can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and compromised patient privacy.
Lack of Data Encryption: Inadequate data encryption practices expose patient data to unauthorized access and interception during transmission which increases the risk of data breaches and privacy violations.
Insufficient Access Controls: Weak access controls and user authentication mechanisms can lead to unauthorized personnel accessing sensitive patient information which compromises data security and patient privacy.
Compliance Challenges: Meeting regulatory requirements such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) poses challenges in data protection, privacy management, and compliance with data security standards.
Healthcare Interoperability Solutions
Robust Data Encryption: Implement strong encryption algorithms and protocols to protect patient data at rest and in transit. Encrypt sensitive information such as medical records, diagnoses, and treatment plans to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Strict Access Controls: Implement role-based access controls (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and least privilege principles to ensure that only authorized personnel can access patient data based on their roles and responsibilities.
Auditing and Monitoring: Deploy auditing mechanisms and real-time monitoring tools to track access to patient data, detect suspicious activities, and respond to security incidents promptly. Performing routine security audits and vulnerability assessments can detect and mitigate potential threats effectively.
Compliance Management: Adhere to regulatory requirements such as HIPAA and GDPR by implementing privacy policies, data protection measures, and security controls.
Challenge 4: Managing Inconsistent Information
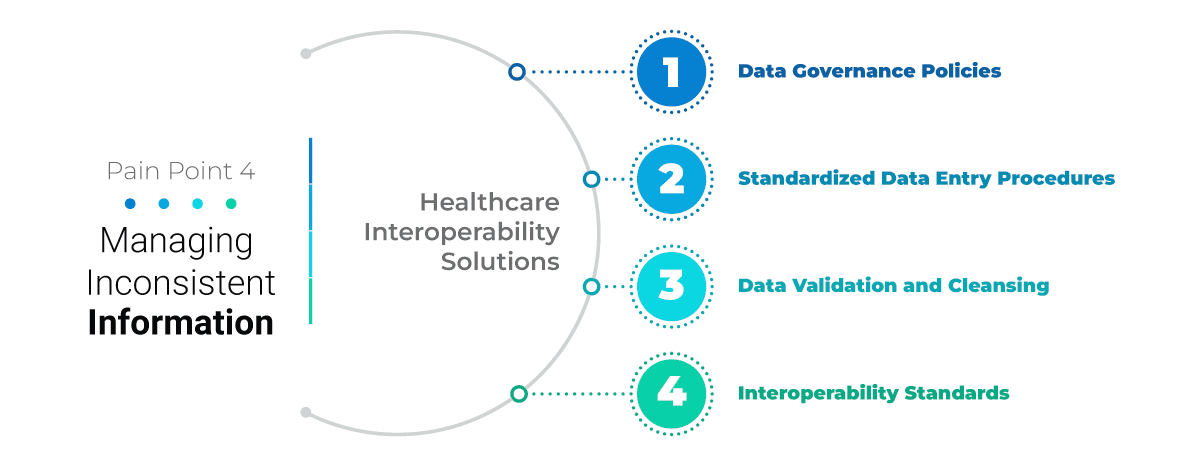
Variations in Data Entry Practices: Different healthcare professionals may use varying data entry practices which leads to inconsistencies in how patient information is recorded and documented.
Terminology and Coding Differences: Diverse terminologies, coding systems (e.g., ICD-10, CPT), and clinical documentation standards can result in discrepancies in how medical conditions, procedures, and treatments are documented and interpreted.
Data Quality Issues: Inaccuracies, duplications, missing data elements, and outdated information can compromise the quality and reliability of healthcare data which impacts decision-making and patient care outcomes.
Interoperability Challenges: Inconsistent data formats, structures, and semantics hinder interoperability efforts which makes it challenging to exchange data seamlessly between separate systems and applications.
Healthcare Interoperability Solutions
Data Governance Policies: Robust data governance policies and frameworks are required to govern how healthcare data is managed, accessed, stored, and shared. Define data quality standards, data integrity guidelines, and data stewardship roles to ensure consistent data practices and standards compliance.
Standardized Data Entry Procedures: Implement standardized data entry procedures, templates, and documentation guidelines across healthcare systems and departments. Train healthcare staff on proper data entry techniques, terminology usage, and coding standards to improve data accuracy and consistency.
Data Validation and Cleansing: Use data validation tools, automated checks, and data cleansing processes to identify and correct inconsistencies, errors, and anomalies in healthcare data. Perform regular data quality assessments and audits to maintain data accuracy and completeness.
Interoperability Standards: Adopt interoperability standards such as HL7, FHIR, and DICOM to facilitate seamless data exchange, integration, and interoperability between healthcare systems, devices, and applications.
Challenge 5: Validating Electronic Requests
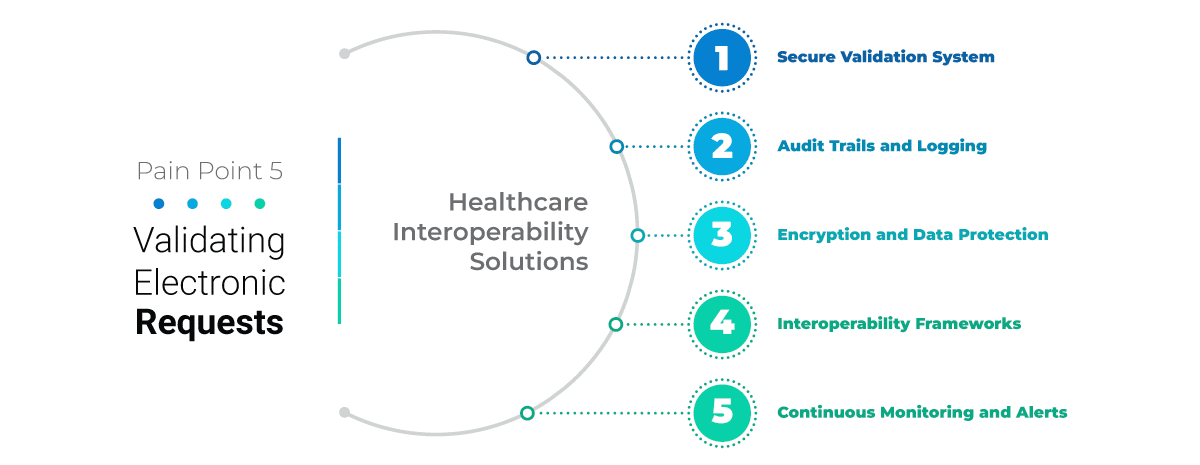
Unauthorized Data Access: There is a risk of unauthorised individuals or entities gaining access to patient data without robust validation mechanisms which leads to privacy breaches and data misuse.
Data Integrity Concerns: Invalid or fraudulent data requests can compromise data integrity, accuracy, and confidentiality which impacts patient trust and healthcare outcomes.
Compliance Requirements: Meeting regulatory requirements such as HIPAA, GDPR, and other data privacy laws approves implementing secure validation processes to protect patient information and maintain legal compliance.
Healthcare Interoperability Solutions
Secure Validation System: A secure validation system can verify the legitimacy and authorization of electronic requests for patient data. Authentication methods such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), digital signatures, access controls, and user permissions can validate requests and ensure data security.
Audit Trails and Logging: Maintain comprehensive audit trails and logging mechanisms to track and record data access activities, including request validation, user authentication, data retrieval, and system interactions. Audit trails provide visibility into data access events, support monitoring and detecting unauthorized access attempts.
Encryption and Data Protection: Encrypt sensitive patient data to protect it from unauthorized access and interception. Implement data encryption standards, secure communication protocols (e.g., TLS/SSL), and data masking techniques to safeguard data during transmission and storage.
Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC): Implement RBAC policies to grant access
privileges based on users’ roles, responsibilities, and permissions. Define access levels, restrictions, and authentication requirements for different user categories to ensure appropriate data access and minimize risks.
Continuous Monitoring and Alerts: Deploy continuous monitoring tools and alerts to detect real-time suspicious activities, anomalies, and unauthorized access attempts. Set up alerts for unusual data access patterns, failed authentication attempts, and security incidents to enable prompt response and mitigation actions.
Wrapping Up
Addressing healthcare interoperability challenges is important for achieving immaculate integration and improving patient care outcomes. However, we have also discussed effective healthcare interoperability solutions. Organizations can pave the way for a more connected, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare ecosystem by adopting these healthcare interoperability solutions.






