Maximizing Patient Care Through Interoperability in Healthcare: A How-To Guide
Maximizing Patient Care Through Interoperability in Healthcare: A How-To Guide
June 24, 2024
In today’s rapidly evolving healthcare industry, the role of technology in enhancing patient care has become important. One of the key pillars of this technological advancement is interoperability in healthcare.
Interoperability services play a vital role in our interconnected environment as it is characterized by the widespread use of diverse systems, devices, and applications for innumerable tasks. Leveraging interoperable systems, devices, and applications is key for healthcare organizations to optimize operations, enhance productivity, and deliver improved services to their clients.
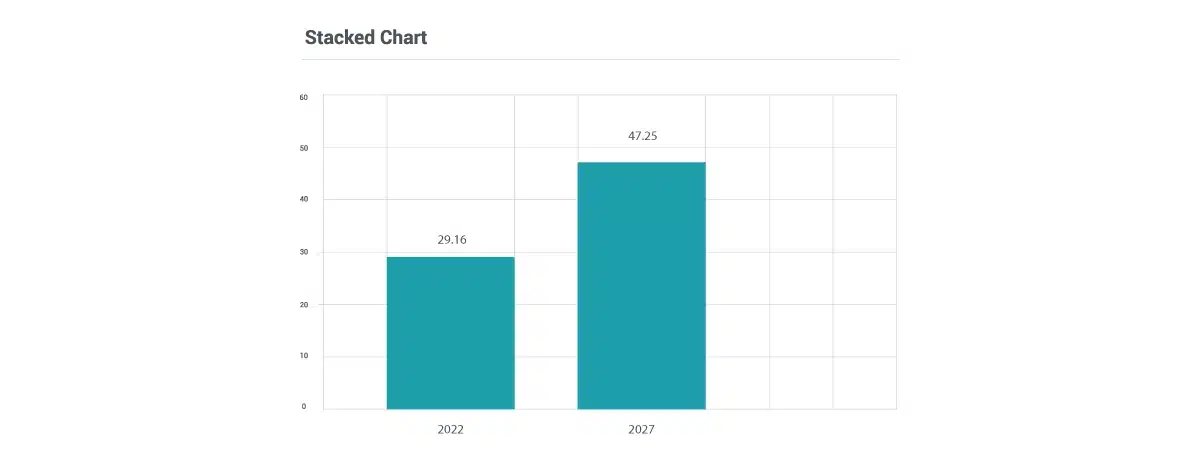
According to research by Facts & Factors, the Global healthcare data interoperability market is expected to reach a value of USD 4.5 Billion by 2026 with a growth rate of 12.9% CAGR.
Further, we will delve into various realms of interoperability in healthcare which enhances the well-being of patient care.
What is Interoperability in Healthcare?
Interoperability in healthcare refers to the ability of different healthcare systems, devices, and organizations to seamlessly exchange and share information. It includes electronic health data, medical records, test results, and other relevant information that can be accessed and used across various platforms and applications. Interoperable systems ensure that data can be accurately interpreted, exchanged securely, and used cohesively to optimize health outcomes.
Importance of Interoperability in Healthcare
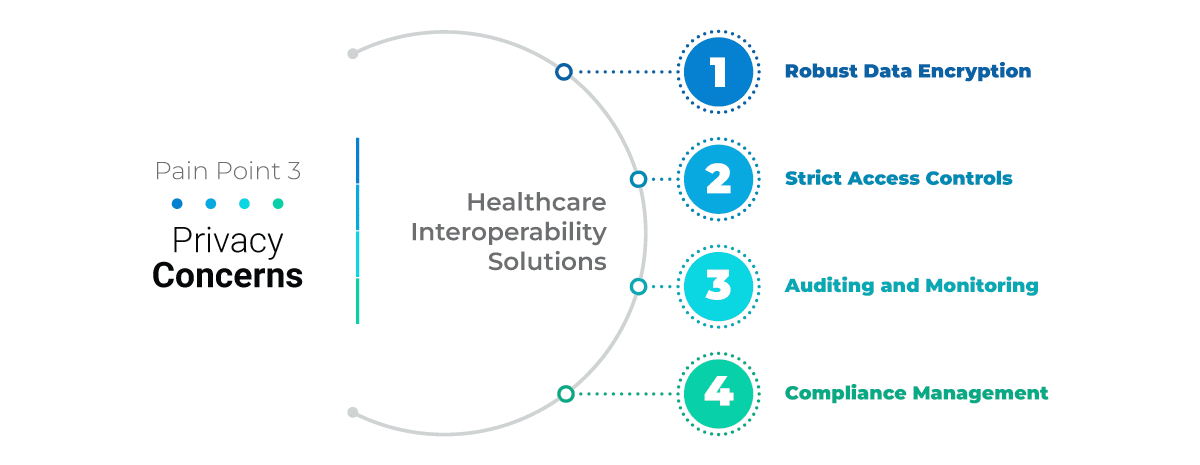
Accessing and sharing health data has always been challenging due to its sensitive nature as it requires strict privacy and security measures. It comes with a dilemma that if this data fails to secure access can lead to significant harm. Such issues in interoperability result in an incomplete understanding of individuals’ health needs which leads to suboptimal outcomes and increased costs.
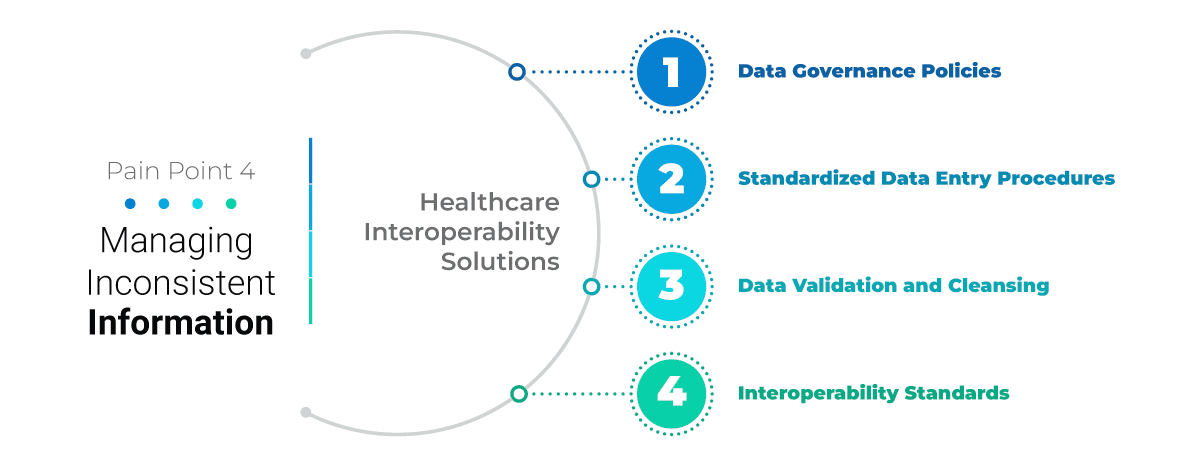
Despite the rise in electronic health record (EHR) usage, integration remains a challenge. While many hospitals can access external data, its integration into patient records often comes across as a difficult task. With interoperability in healthcare, health professionals not only provide comprehensive patient care but healthcare organizations understand utilization rates, meet population needs and drive informed research.
Enhanced interoperability shifts the focus from fragmented data views to holistic patient care models, improving safety, and enhancing overall healthcare experiences.
Major Examples of Interoperability in Healthcare

Interoperability in healthcare refers to the seamless exchange and utilization of health data across various systems, tools, and entities.
Here are some practical examples of interoperability in healthcare:
- Digital Health Records (DHRs) and Health Data Exchange (HDX): DHR systems enable the secure sharing of patient information among healthcare providers and HDX networks which facilitates smooth data flow across different healthcare settings.
- Fast Health Data Transfer Standards (FHIR): FHIR serves as a framework for sharing electronic health records (EHRs) between systems, enhancing communication and compatibility among EHR platforms and supporting data integration from diverse sources such as mobile devices and wearables.
- Telehealth and Remote Monitoring: Integrated platforms allow remote patient monitoring and seamless data sharing between patients and healthcare providers which enables virtual consultations and remote management of chronic conditions.
- Medical Assistance Software (MAS): Functional MAS platforms provide immediate access to medical resources, medication reminders, and personalized recommendations for healthcare professionals. Hence, it enhances care quality and ensures patient safety.
Benefits of Interoperability in Healthcare

Health interoperability serves as the foundation for healthcare providers which enables them to gain a comprehensive and real-time understanding of a patient’s medical history. This capability empowers informed decision-making, reduces the risk of medical errors, and enhances the overall quality of patient care.
Likewise, healthcare interoperability offers significant advantages to all participants within the healthcare ecosystem.
Here are the key benefits of healthcare interoperability for patients, healthcare professionals, physicians, and the healthcare industry as a whole.
- Continuity of Care: Patients often receive treatment from multiple healthcare professionals across different locations. Interoperability is vital in ensuring the seamless exchange of health information which guarantees consistent care delivery and prevents treatment disruptions.
- Improved Efficiency: Streamlining data sharing among various healthcare systems reduces manual work, paperwork, and redundant tests. It not only saves time but also decreases errors associated with manual tasks.
- Cost Savings: Healthcare interoperability leads to cost benefits by eliminating repetitive tasks, reducing errors, and optimizing resource utilization. It encourages efficient healthcare spending management.
- Patient Empowerment: Interoperability empowers patients by providing them with expanded access to their health data, promoting transparency, and encouraging active participation in healthcare decisions. It fosters adherence to treatment plans and empowers individuals to take control of their well-being.
- Advancing Public Health: Interoperability plays a crucial role in advancing public health initiatives by facilitating rapid data exchange on disease outbreaks, monitoring health trends, and implementing preventive measures. All of these are collectively aimed at enhancing population health management.
- Streamlined Administrative Processes: Automation of administrative tasks in healthcare reduces the workload for medical professionals. It includes streamlining billing processes, managing insurance claims, and executing other administrative functions which enhances workflow efficiency.
- Enhanced Data Analytics: Healthcare data interoperability enables comprehensive data analytics, providing valuable insights into public health, treatment effectiveness, and trends within the healthcare landscape. Such a data-driven approach supports informed decision-making and long-term strategic planning.
How to Improve Interoperability in Healthcare
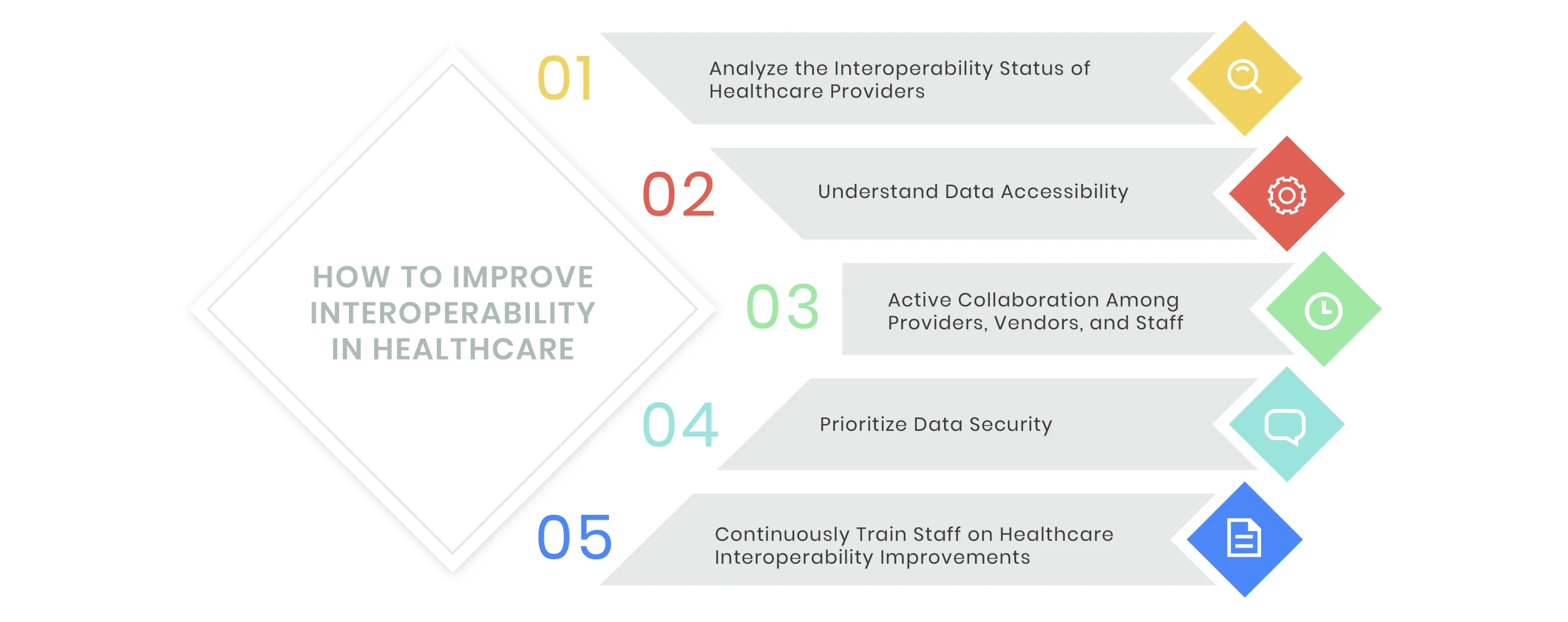
Improving interoperability in healthcare involves several key strategies:
Analyze the Interoperability Status of Healthcare Providers
With newly established standards for healthcare interoperability, challenges arise when organizations or vendors fail to align with FHIR standards. Many times these misalignments hinder healthcare tech vendors from accessing and integrating essential data. To achieve desirable or correct results, healthcare tech teams should evaluate how hospitals and practices perform with interoperable systems. Understanding and implementing changes according to industry standards is crucial to fully utilize these advancements such as EHR and EMR.
Understand Data Accessibility
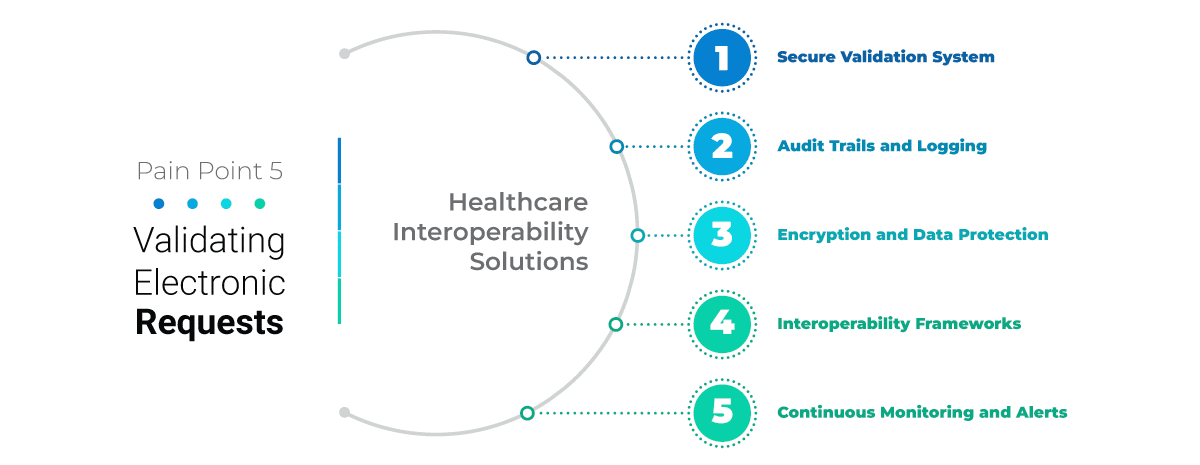
Nowadays, it is important to utilize standardized APIs in the health sector. It enables various systems to communicate seamlessly and allow individuals secure access to health information through mobile phones and other digital devices.
One of the significant challenges for healthcare tech vendors is not knowing what data is available, whether it comes from a source system, what the data means, or where it is located. Therefore, organizations must define the type of data they have, what data they plan to exchange, where it needs to be transmitted, and how the recipient systems will use it before data exchange.
Active Collaboration Among Providers, Vendors, and Staff
Improved EHR usability and interoperability requires transparent collaboration between vendors and healthcare organizations. This collaboration is crucial not only during the implementation phase but also for ongoing interoperability efforts. For instance, a primary care practice needs to accurately enter and extract EHR data to generate quality measures and other metrics.
Ensuring that teams across health technology systems develop an effective method for integrating EHR data is crucial. This approach is a key step in enhancing care delivery and patient outcomes through collaboration.
Prioritize Data Security
Data security is important in healthcare. A lack of comprehensive security measures can jeopardize patient records which can put lives at risk. To achieve interoperability, security must be prioritized in the development process. Healthcare stakeholders must build trust and align health systems and plans to strengthen secure healthcare information exchange.
Implementing a secure API approach to enhance interoperability will help create a robust health IT system focused on quality care. A team with diverse skills is vital for developing a secure, interoperable system that considers the user experience.
Continuously Train Staff on Healthcare Interoperability Improvements
Successfully upgrading systems often requires significant involvement from healthcare providers. Involving staff during system improvements ensures they can smoothly adapt to changes and understand their benefits. For healthcare interoperability, familiarizing medical staff with interoperability tools allows them to efficiently retrieve and share necessary information. This reduces workloads, facilitates the transition to digital systems, and improves patient activity documentation.
How Interoperability in Healthcare Empowers the Future of Patient Care
Advances in interoperability and connectivity are paving the way for a more integrated and efficient healthcare system. To fully realize these benefits, it is crucial to overcome existing barriers to interoperability and leverage the potential of interconnected health systems. Such a big change can enhance patient experience through several key improvements.
Facilitate Care Coordination
Interoperable systems allow for seamless communication and information exchange among healthcare providers. It enhances care coordination, reduces fragmentation, and ensures that all members of a patient’s care team are well-informed and on the same page.
Enhance Patient Engagement
When patients have access to their comprehensive health records, they become more empowered to participate in their care. Their involvement includes making informed decisions, collaborating effectively with healthcare providers, and sharing vital health information, all of which contribute to improved care outcomes.
Improve Patient Safety and Reduce Medical Errors
Comprehensive and accurate patient information is essential for healthcare providers to make well-informed decisions. This reduces the risk of medication errors, allergy mishaps, misdiagnoses, and other adverse events.
Proper Knowledge of Patient’s Condition
Real-time clinical information ensures that providers are fully aware of their patients’ histories and needs. This not only reassures patients that they are known and valued but also minimizes the need for them to repeatedly share their medical histories, thus respecting their time and enhancing their overall care experience.
Conclusion
Interoperability in healthcare is the top priority for health experts all over the world. Improving patient care through interoperable systems is not only a technical upgrade but a transformative approach to healthcare. By facilitating seamless data exchange, these systems enhance patient safety, streamline workflows, and improve clinical outcomes. Ensuring that healthcare providers have access to comprehensive patient information empowers them to make informed decisions, reducing errors and improving the quality of care