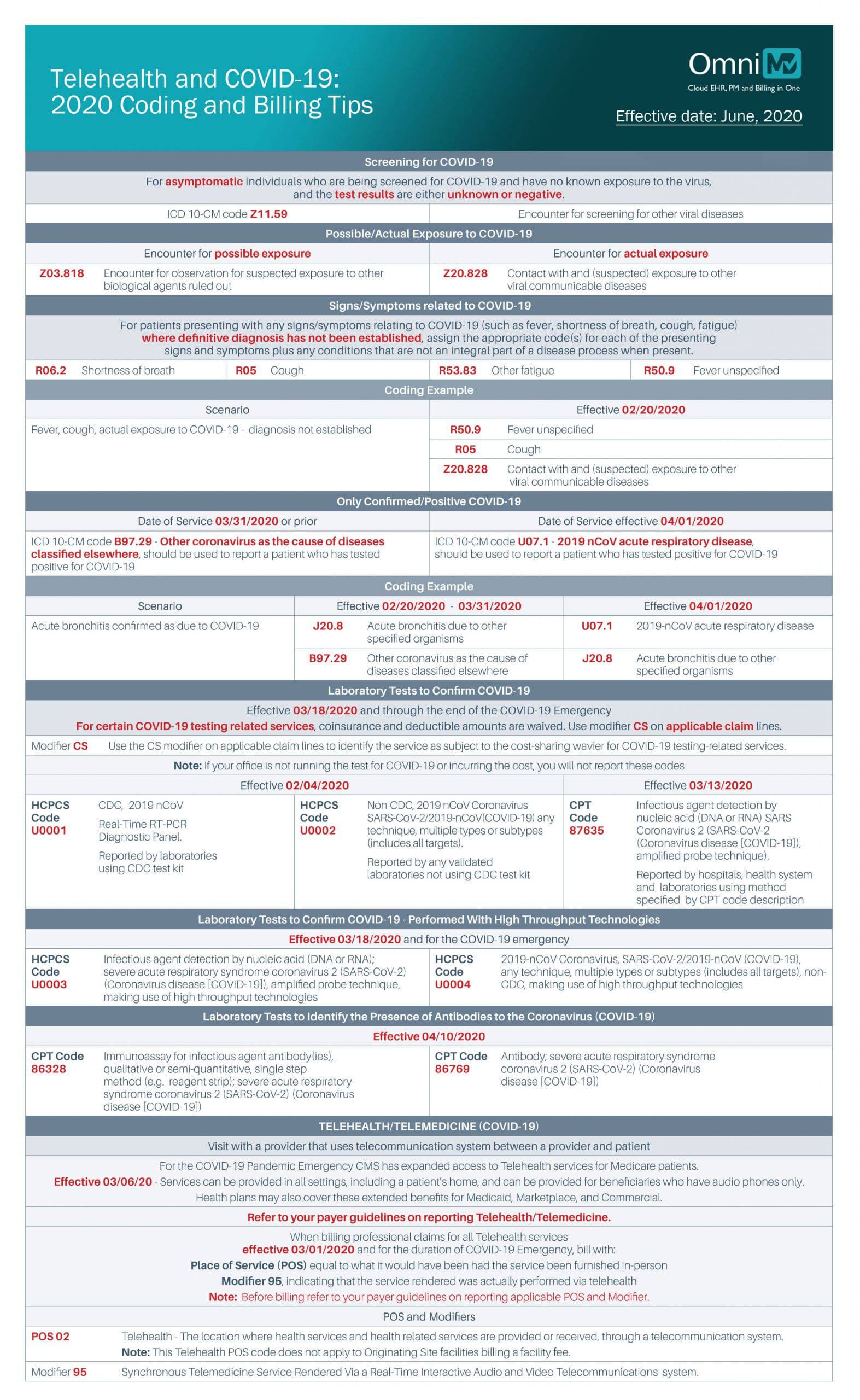
Telehealth and Covid-19: 2020 Coding & Billing Tips



December 3, 2020
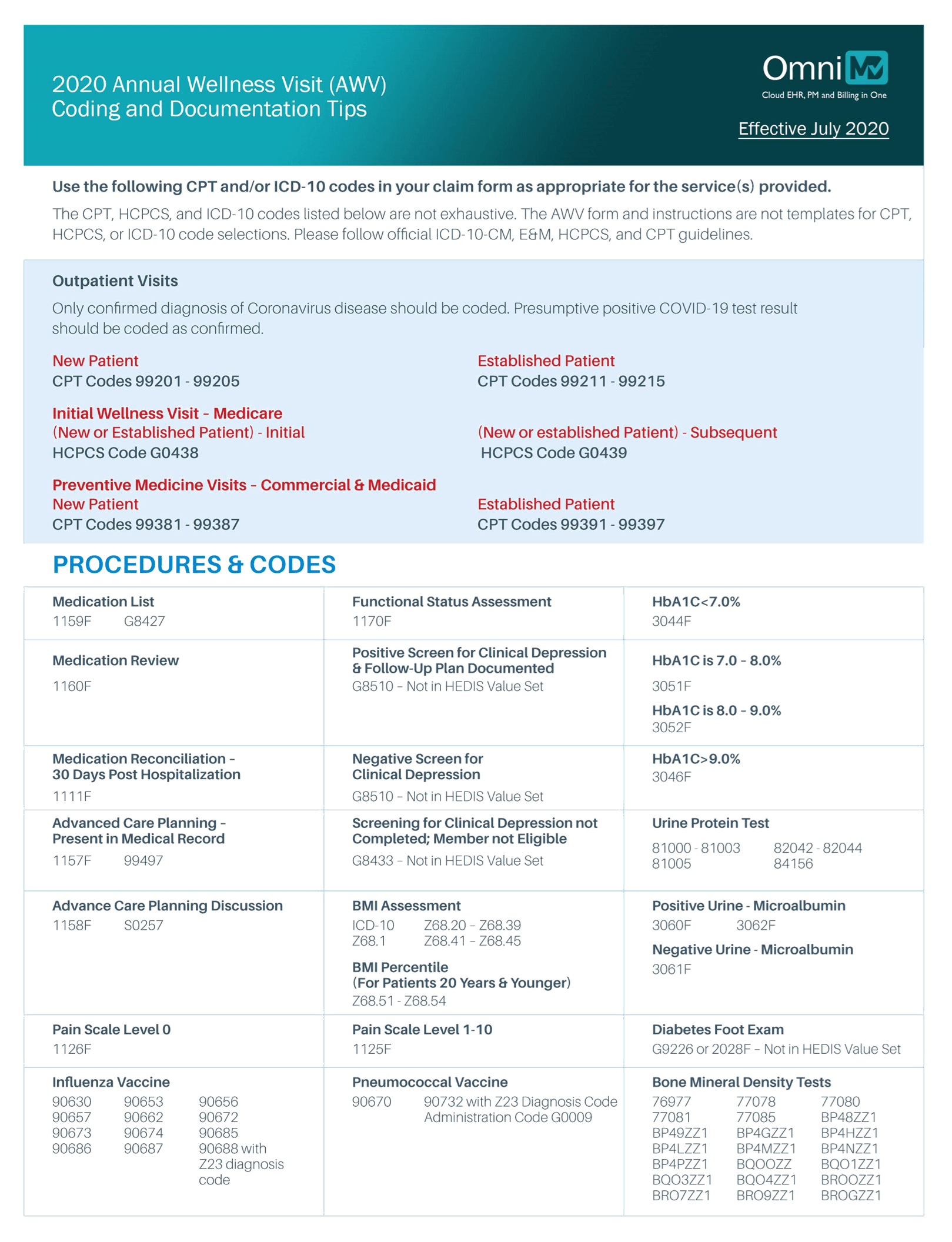
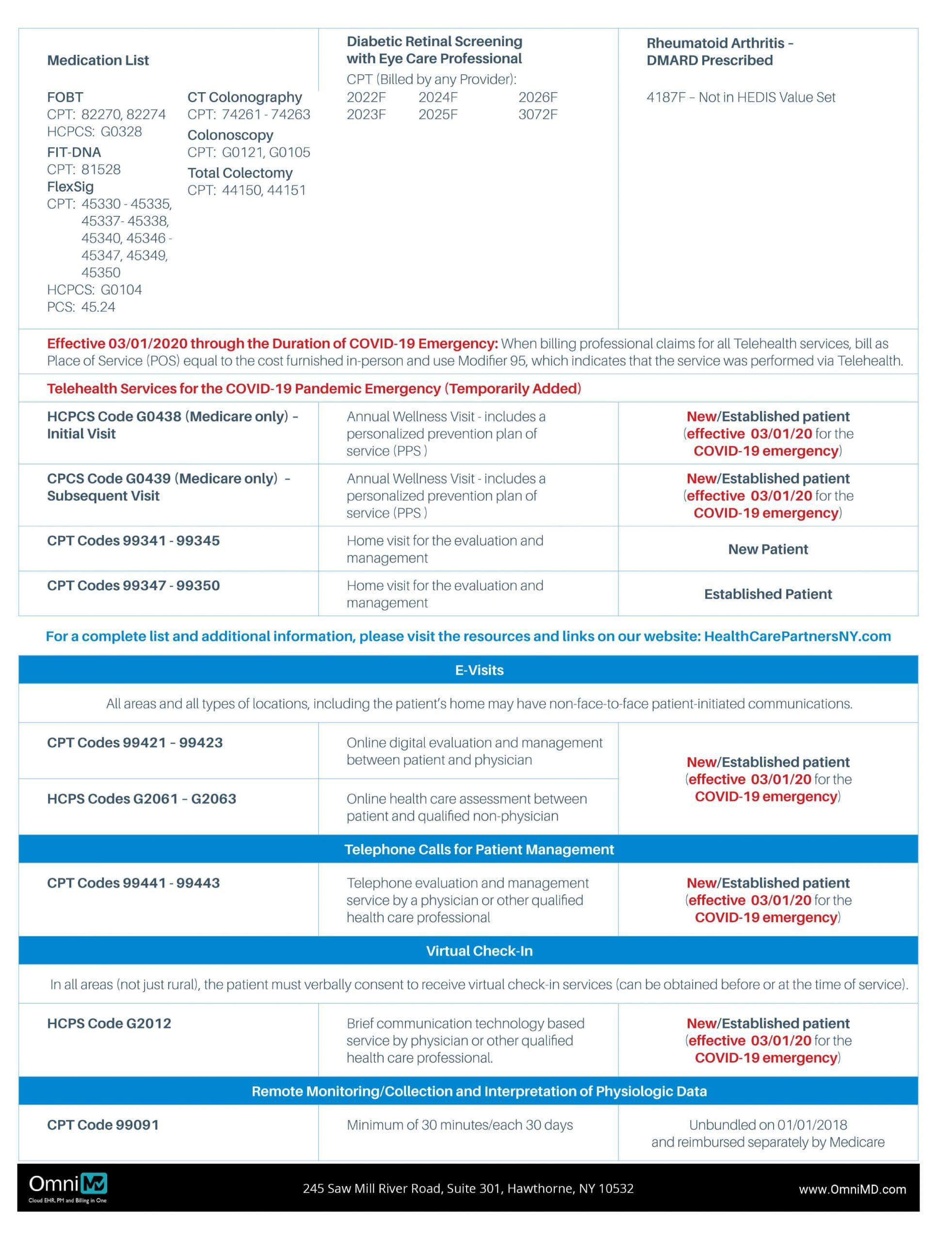
2020 Annual Wellness Visit (AWV) Coding and Documentation Tips
Coding and Documentation Tips

December 2, 2020
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has embraced the recommendations of the AMA in regards to Evaluation and Management (E&M). Starting January 1, 2021, these changes will be applicable for coding office and other outpatient services.
In 2017, CMS brought an initiative “Patients Over Paperwork” to streamline work, increase efficiency, improve patient experience, and reduce administrative burden.
The purpose of this initiative was to revise the existing and archaic E&M coding guidelines. According to CMS, increasing paperwork and reporting tools were the main bottlenecks that kept physicians and medical practices busy.
They were required to spend more time managing administrative tasks instead of caring for patients. It resulted in poor patient experience and monumental administrative tasks that added to the cost as physicians needed to hire additional staff and comply with the government rules and regulations.
History and Tests Removed as Mandatory Elements for Coding. These two components tend to delay clinical decision making and are time-consuming as the clinicians need to document this in the patients’ medical record.
Physicians cannot use both these documentation methods for the same patient visit. They need to select either option for each patient visit.
Time is explained as “total time on the date of the encounter.” It includes time spent by authorized healthcare professionals and clinicians for in-person and other modes or non-face-to-face discussions with the patient.
It should be used for time-based coding when the duration of the encounter exceeds the defined time for 99205 and 99215 in 15-minute increments.
Using the present CMS Table of Risk as a standard guideline, the MDM elements for code selection were refined and clarified to avoid complexity and increase efficiency patient management.
Considering the RVU guidelines from the AMA’s CPT/RUC Workgroup on E&M, CMS has stated that relative value for the codes is evaluated depending on the total duration spent by a physician from three days before patient’s visit through seven days following the visit as the standard work will be same irrespective of the time when it is completed.
Source: https://www.ama-assn.org/

November 10, 2020
Effective revenue cycle management is the foundation of every medical practice. But what is the impact of medical billing errors on a healthcare practice? As healthcare providers, you are aware of the high cost of care and the competitive market. High medical claim denial rates can affect the bottom-line and reduce your revenues significantly.
Whether your practice is big or small, you can’t be casual about medical billing errors that could easily be prevented. Yet, small and independent practices have more to lose when it comes to billing errors.
A 2014 Advisory Board study reveals that 90 percent of claim denials are preventable. Practices need to build a prevention-focused claims management approach, use automated processes, use data to analyze claim denial reasons, and improve their front-end revenue cycle management process.
Fortunately, if you are cautious, you can avoid these common medical billing errors easily. In this article, we run through the most common billing errors and how you can avoid them.
The Error:
Coverage availability is one of the most common areas where practices tend to slip up. A recent Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) survey shows that 76% of healthcare leaders find denials to be their biggest challenge. Healthcare practices can be more effective in reducing denials by using analytics to determine the leading causes of denials.
The study found that a breakdown in the front-end processes causes some of the most common denials. For instance, patient registration and eligibility errors alone account for 23.9%.
One of the easiest ways to avoid denials is being accurate with crucial information when it comes to EV and BV.
Many practices that depend on in-house resources for Eligibility and Benefit Verifications miss out on key information because they focus on moving the transactions. They lack the software and the know-how to audit real-time eligibility information based on individual player rules and denial patterns. And by the time you realize this, and the claim is denied, it is too late.
The Solution:
You need a system that provides automated eligibility verification and benefits mapping to take the guesswork out of the process. Technologies such as ours can reduce your eligibility denials by 50% by offering eligibility verification in real-time and alert you on coverage, coordination of benefits, policy termination, the correctness of demographics, co-pays, and deductible. A good technology platform will provide not only real-time checks but scheduled eligibility rechecks, batch eligibility checks and verify co-pay, co-insurance, and deductible information.
There are many benefits of a streamlined verification process.
The error and its impact:
Duplicate billing or double-billing is when claims are resubmitted for a single encounter for the same date by the same practice. These are among the top reasons for Medicare Part B claim denials (up to 32%).
The actual cost of duplicate billing goes beyond the revenue. There is a delay or loss in payment, reputation loss, and the possibility of fraud investigation.
Wonder why duplicate claims submission is so rampant across the industry? It is because most practitioners use a reactive medical billing process. According to Health Payer Intelligence, 46% of medical fraud cases in 2016 were due to either fraudulent provider billing or double-billing, costing a whopping $29 million in fines.
An intuitive technology revenue cycle software can alert you and help reduce manual errors and outdated information and keep your data clean, so there are no duplicate or double-billing chances.
The Error:
Often an in-house staff will enter mismatched treatment and diagnosis codes. Usually, this happens when the biller upcodes the diagnosis without updating the treatment code. Insurance companies typically reject such claims, or sometimes the claim is inflated due to upcoding.
Another possibility is that the insurance company will reject the claim due to a lack of medical necessity. Problems occur because the biller and coder must have a thorough knowledge of ICD-10-CM codes and CPT codes for the procedure.
For example, using the code for a bunion procedure when the only diagnosis is asthma.
The Solution:
Physicians need to provide coders with the necessary information about the patient’s diagnosis. It requires comprehensive documentation and detailed patient records with all possible information, including accompanying conditions for better application of codes.
Invest in ongoing training and education programs and informal coaching to ensure that employees know the latest coding requirements.
Luckily, advanced billing software can help you avoid these errors by automatically suggesting the right ICD codes based on common diagnosis and keywords entered.
Choose technology wisely and invest in a system that codes to the highest specificity levels, ensuring that your claim is not denied.
The Error:
To err is human. Data entry errors are more common than one can imagine. Incorrect information in your claim will lead to claim denial. From the practice address, the phone number to the patient’s name, gender, birthday, and insurance details to the insurance company’s address and policy number, there are many places where billers goof up.
Manual data entry errors contribute the largest percentage from 23.9% claims denied due to eligibility errors and registration issues and other 12.4% owing to incomplete or missing authorizations.
The Solution:
Software scrubbing can eliminate such manual and basic coding errors quite easily. For instance, if a wrong zip code is entered or an incorrect format for member ID is entered, the software will immediately prompt the relevant error messages.
The Error:
While billers work hard to reduce claim denials, payers have, over the years, increased the number of visit types and procedures that need prior authorization or pre-authorization. It has led to a rising number of denials in most procedure-based practices.
The MGMA’s recent stat poll reveals prior authorization errors to be the leading cause for denials when respondents were asked, “What is the root cause of claims denials/pends?” About 31 percent answered “pre-authorization.”
A December 2017 study from the American Medical Association states that 86 percent of physicians have reported that prior authorizations have increased in the previous five years, whereas 51 percent report they have increased significantly.
The Solution
You need to be ahead of the game and use medical billing software that can help you set alerts on plans mandatorily requiring pre-authorization and referral numbers, missing, which leads to denial and loss of significant revenue for higher value procedures.
The Error:
If you are confident that your process was foolproof, but your claim has still been rejected.
Sometimes, it is the insurance company that makes a mistake. If you have reviewed your claim’s accuracy, then it is likely that the payer made a mistake.
And going by recent reports, the overall rates of inaccurate claims payments have been increasing. As per AMA, claims processing errors by insurance companies cost practitioners billions of dollars. Not to mention the frustration and avoidable delays. AMA’s latest findings show that commercial health insurers have an average claims processing error rate of 19.3 percent. This overall inaccuracy amounts to $1.5 billion in unnecessary administrative costs to the healthcare ecosystem. AMA estimates also show that eliminating payer mistakes could potentially save $17 billion.
The Solution:
An excellent way to find out if there has been a mistake on your claim from the payer’s side is to review the denial statistics. As a best practice, all physician’s offices must keep track of monthly denial reports to reveal patterns.
A medical billing reporting tool can help you speed up things by providing the requisite data and reports that make it easier to spot issues. You can easily confirm whether the claim was denied owing to a payer error using these reports.
The Error:
Under coding means billing for a less expensive service than the actual treatment performed or missing out on billing the codes all together. This error affects your practice’s bottom line but may also have legal repercussions from the audit perspective. In 2016 alone, the Medicare fee-for-service improper payment rate was an estimated 11 percent or nearly $40.4 billion.
The Solution:
Double-check patient information before filing the claim and ensure safety nets and peer reviews for maintaining accuracy. Always review the superbill and chart to make sure each procedure has been accounted.
Fortunately, with an audit form with medical billing software, you don’t have to worry about under coding or the potential risk of fraud implications.
The Error:
Upcoding or over-coding is when a practice bills the patients for services they haven’t received or services that were more expensive than what they were treated. It may happen for two reasons: accident or when the diagnosis and treatment codes are mismatched.
Unfortunately, some providers also do this to inflate the total amount a patient owes. It is considered fraudulent, and practitioners must be wary of upcoding, whether by accident or design.
A psychiatrist was fined $400,000 and permanently excluded from participating in Medicare and Medicaid in part due to upcoding.
The Solution:
Stay updated on billing and coding trends. Update your procedures and invest in your employees’ training and education. Be sure your billing team understands the latest updates in medical billing codes, modifications in healthcare regulations, new illnesses, or new treatments for diseases.
Medical billing software with inbuilt audit forms can also help you mitigate these errors as the software updates take care of the latest codes and regulations.
The Error:
Unbundling is the process of billing for individual services that are covered under a less expensive packaged treatment plan. It means that the charges that should be grouped under one code are listed separately, leading to an inflated package rate. Unbundling happens due to negligence or improper billing standards.
However, unbundling is more common than we can imagine. Unbundling was identified as one of the most common medical billing errors by the AMA in 2018.
The Solution:
Practitioners can avoid unbundling errors by making sure tricky scenarios where coders can easily slip up. Investing in the right technology solutions to create payer-wise charge templates can help you avoid this error.
Key Takeaways for Operational Efficiency and Revenue Discovery & Recovery
Medical billing errors are shockingly common, and both practitioners and patients end up paying a heavy price for these mistakes. These errors are hurting healthcare as a whole, and the damage often goes beyond monetary loss by compromising the facility’s reputation or practice.
Here are some ways in which healthcare practitioners can be more cautious and proactive when it comes to claims denials:
A state-of-art revenue cycle software and caring medical billing service can easily help you prevent these ‘avoidable errors.’ Invest in the modern-day right technology and the right resources to spot these mistakes and improve your operational efficiency and revenue.

November 9, 2020
The U.S. medical billing outsourcing market size is predicted to reach USD 7.8 billion by 2026. Factors like a growing burden on revenues and profits, declining Medicare payments, and escalating billing volumes have led to the need to decrease in-house processing expenditures. However, before we take a comparative analysis of the pros/cons of both, it is essential to complete a cost-benefit analysis, the cost of billing in house versus the cost of contracting the service outside. Consider resources, training, technology, infrastructure, and other resources when calculating your in-house expenditure on billing.
In-house billing versus Outsourced Billing: What should you opt for?
The success of any healthcare practice depends heavily on optimal billing. Is the healthcare facility competent enough to handle diverse functions? Hospitals are already facing a decline in revenues due to shrinking margins, reduced reimbursements, and staffing problems.
Outsourcing RCM and billing is increasingly becoming the smarter choice for doctors. Even the smallest of practices can benefit immensely with improved patient care, dedicated focus on patient cycles, and improved ROI. According to the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA), nearly 50-65 percent of denials are unaddressed. It doesn’t just mean loss of revenue; it also has a long-term impact on your practice. With outsourced billing, you can streamline your practice and make it more patient-centric. Here’s a detailed look at the pros and cons of in-house versus outsourced billing.
Many doctors, healthcare practices like to retain control over the financial operations by keeping them in-house and find it easier to trust their trained resources carrying out the billing. Easier access Having instant access to your in-house billing department is often considered a significant benefit of keeping things in the house. All it takes is a walk across the floor to address the query or problem at hand.
One primary concern is over data protection and confidentiality. Some medical specialties find it safer to keep the billings in-house due to sensitive nature and patient-doctor confidentiality.
In-house billing startups and smaller practices mean many upfront expenses such as labor, technology, hardware, billing software, and training. Besides, it means ongoing overheads for maintaining the system and hiring resources. Also, consider the office and rental space for employees, workstations and filing cabinets, etc.
Further, medical practices incur many expenses on benefits rendered, such as vacation pay, insurance, workers’ compensation, etc.
You need to hire and train the right kind of billing personnel. If the personnel is not up to date, it can harm your billing cycle, including rates of denials, un-appealed claims, and lower reimbursement rates.
If you are short of staff due to absenteeism or attrition, it impacts billing productivity and cash flow. Hiring staff and ongoing training are also an additional responsibility.
By outsourcing medical practice, you can focus on your core activity of medical practice. Since medical billing needs a lot of time, effort, and resources, it becomes an additional headache for the practitioner to manage.
With updated RCM technology and analytics, you have improved patient care, dedicated focus on the patient cycle, and increased cash flow with better optimization prospects.
Healthcare compliance has legal, ethical, and reputational elements to it that require expertise. The regulations cover several billing and reimbursement issues, processes, policies, HIPAA laws, and other rules as applicable. An outsourcing partner with a team of experts is better equipped to meet these regulations better.
Outsourcing billing is cost-effective but more so if you are starting up or have a smaller practice. Keeping billing personnel and software up to date with the latest rules and regulations is time-consuming and quite challenging.
The right billing company and software can generate comprehensive reports and insights. It provides doctors with insights and better visibility of the status without having to micromanage employees.
Outsourced billing companies are experts and experienced in this domain. Therefore, they can identify denial trends, other anomalies, and challenges better than in-house staff.
Many medical practitioners are concerned about the loss of control and privacy when sharing critical patient information.
HIPAA security and privacy concerns are another valid concern when outsourcing the billing as any breach in compliance can adversely impact the practice. However, many solutions like Omni MD’s medical billing service are fully compliant and improve your operational efficiency with an integrated MU, ONC-ATCB, MACRA-enabled EHR system with an exceptional billing tool outstanding service solution.
Not all outsourced companies are equal. There is a great deal of research involved in selecting the right provider. You also need to read all contracts extremely carefully. Ensure there are no hidden charges and also find out if there are any cancellation charges.
While many practitioners prefer to carry on with in-house billing, the outsourced billing advantages are far too obvious. Your time and expertise are better spent on patient care and improving your practice, rather than the nitty-gritty of paperwork and administration. But above all, the cost factor is too hard to ignore. By outsourcing the billing services, practitioners can save anywhere between a few thousand to a quarter-million dollars. Just for a 3-Physician practice, the savings can range up to $200,00. It is easy to find out the potential savings for your practice by using this savings calculator. To find out how effective our system is and how much you could save, please leave a message, and our representatives will be in touch with you. A cost analysis will certainly help you to make a prudent choice.

October 29, 2020
Billing denials adversely affect the operational and financial efficiency of a healthcare practice resulting in higher administrative charges. According to a recent Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) report, 76.1% of healthcare leaders say that denial is the biggest challenge.
By the time your claim gets denied, you have already spent not less than two weeks. Then to appeal a denied claim, you invest additional time, money, and resources. It also means a longer waiting period to receive reimbursements. Cardiology billing denial is no exception.
With more insurance companies imposing stricter eligibility criteria for claims submission, cardiologists find it increasingly difficult to receive reimbursements. Wondering why cardiology claims get denied? Some of the most common reasons for cardiology billing denials are:
As outlined by the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA), a practice should achieve a 95% or higher clean claim rate. Interestingly, most practices struggle to achieve a clean rate above 75%. Now even for a small practice that files 2000 claims with a 10% denial rate, it comes to 200 denied claims! According to MGMA, reworking a claim costs $10-$25, translating into a considerable number for these 200 claims.
Given the complexity of these challenges, you should act fast and start with addressing the core issues. To help you understand where it could go wrong, we have shared nine tips. Following these will surely increase the clean claims ratio and prevent denials or audits.
In order to meet timely filing requirements, billers need to make sure their claims are acceptable. A claim can be rejected at any stage, and once it returns to your desk, half the time is gone. Note that your payer is only interested in entertaining your claim when submitted with the required elements necessary for processing and well before the deadline.
Familiarize yourself with the best practices that ensure timely filing of claims to avoid denials:
Most mistakes start with the patient registration process. Avoid entering incorrect patient data and always double-check their date of birth, name or spelling, subscriber number, and other important information before filing. As, managing patient files manually can be challenging and there are chances of misplacing them, you can use an EHR to manage patient information and health records easily, update real-time, and securely share with authorized users. It will also help you avoid repeated paperwork and chances of mistakes.
Accurate coding is critical to achieving claim success. Cardiology practices often face various challenges, such as, entering incorrect or deleted codes, missing modifiers or combination codes, lacking specialty-specific coding experience, and under coding. As a result, claims are either denied or underpaid. Codes like 93880 (non-invasive cerebrovascular arterial study) can be billed twice a year only. 93297 and 93295 cannot be used in conjunction together. To minimize coding mistakes, refer to the latest CPT, HCPCS, and ICD-10 CM and PCS code books. Subscribe to the quarterly newsletter released by the American Heart Association (AHA) to stay informed about the recent updates and changes. Additionally, you should often check for updates with the CMS and local regulatory bodies.
Whether you are rendering service to returning patients or registering new clients, it is necessary to verify the patient’s eligibility and benefits each time.
Pay attention to:
Beware of duplicate filing claims for the same individual, same visit, and same service. Consider periodic audits and remove duplicates. When appealing a denied claim, ensure the necessary corrections. Failing to comply with the rules and resubmitting claims without making proper changes will lead to your claim being denied on the ground of duplicate billing and may even lead to auditing.
According to the 2019 ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting, Section I-B, healthcare practitioners are required to report confirmed diagnoses, if found, and not use signs/symptoms codes (2). The report indicates, “Codes that describe symptoms and signs, as opposed to diagnoses, are acceptable for reporting purposes when a related definitive diagnosis has not been established (confirmed) by the provider.”
Nearly 64% of physicians report it is difficult to determine which tests and procedures require pre-auth by insurers. Many cardiologists lose out on their claim(s) settlement failing to abide by the pre-auth requirements. Several cardiac procedures on the heart and pericardium like ‘pacemaker installation, ‘electrophysiologic’ and/or implantation of hemodynamic monitors, etc., require preauthorization. If you render services that fall under this criterion, verify with the insurance provider, and obtain a preauthorization.
Incorrect documentation can cost your time, revenue, and put you at risk for denials and payer audits. As short-hand notes can be confusing and lack depth, you should ensure complete documentation and transcription. It will help you avoid unnecessary hassle and miscommunication with billers and coders. An Electronic Health Record and Practice Management System can efficiently help you achieve higher accuracy.
Using an advanced revenue cycle management software can significantly reduce administrative errors and billing denials. For example, OmniMD comes with intuitive solutions for cardiologists, and specialty healthcare providers, such as it triggers alerts, generates automated predictive analysis to potential flag denials, offers preauthorization tracking module all in one place. Consider switching to an effective and efficient EHR and Revenue Cycle Management software to enhance your claims filing experience and minimize revenue cycle gaps.
Cardiology billing denial is both unnecessary and avoidable. With the best practices and effective revenue cycle management software, you can surely achieve a higher clean claim rate and prevent denials.